CSGO Flares: Your Ultimate Esports Hub
Explore the latest news, tips, and insights from the world of CS:GO.
Lost and Found: The Hair Story You Need to Read
Discover the shocking journey of hair and identity in Lost and Found. This is the hair story you can't afford to miss!
The Journey of Hair: Understanding Its Growth and Loss
The journey of hair begins at the follicle, where growth occurs in a cyclical process. Hair follicles are small pockets in the skin that undergo three main phases: Anagen, the active growth phase; Catagen, the transitional phase; and Telogen, the resting phase. During the Anagen phase, which can last several years, hair cells divide rapidly, causing the hair to grow. It's fascinating to note that the average human head has about 100,000 to 150,000 hair follicles, with each individual strand having its own unique growth cycle. Understanding this complex mechanism sheds light on why some people experience faster growth or more significant hair loss than others.
When it comes to hair loss, various factors play a critical role, including genetics, hormonal changes, and environmental influences. Conditions such as androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, are directly linked to genetic predisposition. Additionally, stress, poor nutrition, and certain medical conditions can disrupt the natural growth cycle, leading to increased shedding or thinning of hair. It's essential to recognize the different causes of hair loss to seek appropriate treatment or management strategies effectively.
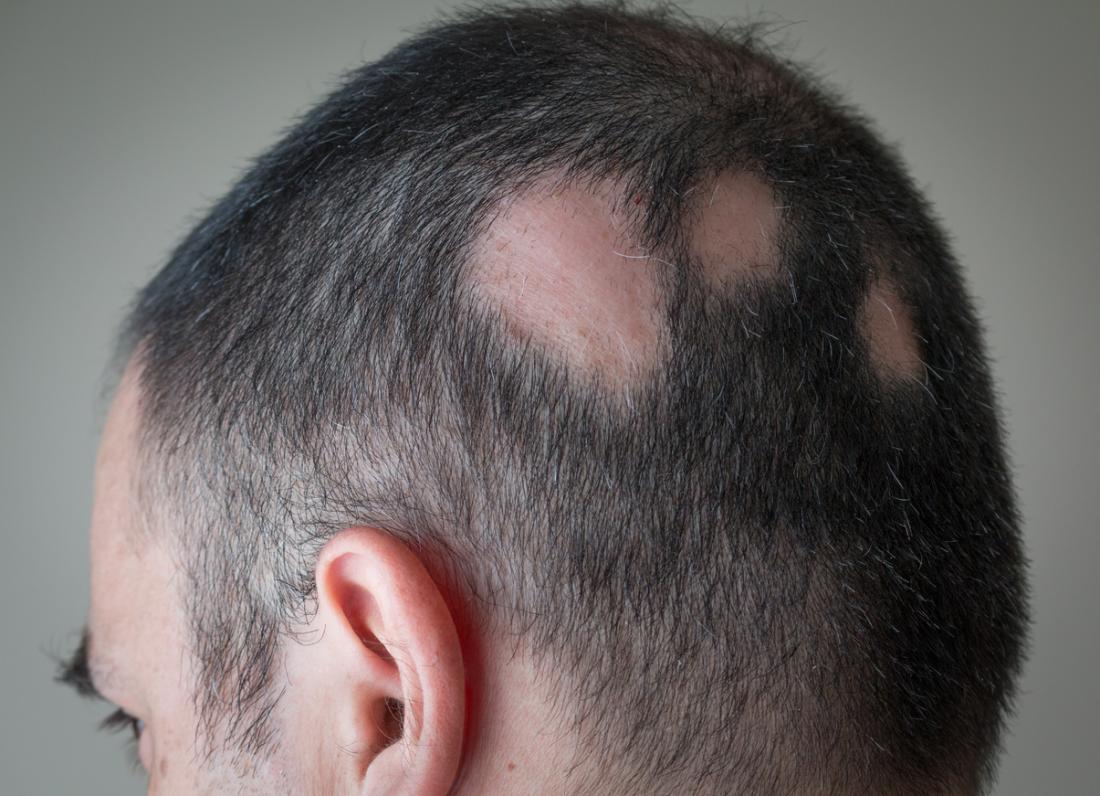
Top 5 Myths About Hair Loss You Need to Stop Believing
Hair loss is a common concern for many, but it's also surrounded by numerous misconceptions that can lead to unnecessary worry. One of the most prevalent myths is that wearing hats causes hair loss. In reality, hats do not affect the hair follicles. They might block sunlight and help maintain a warm temperature, but they do not contribute to shedding hair. Another myth is the belief that only men experience hair loss. While androgenetic alopecia is more commonly recognized in men, women can also experience hair thinning due to hormonal changes, genetics, or medical conditions. It’s essential to understand that hair loss affects everyone, regardless of gender.
Another common myth is the notion that sudden hair loss is always permanent. Many people assume that when they notice a significant amount of hair falling out, it signifies irreversible damage. However, temporary hair loss can occur due to stress, illness, or changes in medication, and many times, hair can regrow once the underlying issue is addressed. Additionally, some people believe that hair loss only happens with aging, while in fact, it can start at any age due to various factors like genetics and lifestyle. By debunking these myths, individuals can better understand their hair health and approach solutions without unnecessary panic.
What to Do When You Start Losing Hair: A Comprehensive Guide
Experiencing hair loss can be a distressing and challenging situation, but it's important to approach it with a level head and take proactive steps. The first thing to do is assess the situation. Determine whether you're experiencing gradual thinning or sudden patches of hair loss. Keeping a journal of your grooming habits and any changes in your lifestyle can help identify potential triggers. If you notice consistent shedding, consider scheduling an appointment with a dermatologist or a trichologist who specializes in hair and scalp conditions. They can perform tests to diagnose the cause of your hair loss, whether it be genetic, stress-related, or a medical condition.
Once you understand the reasons behind your hair loss, explore various treatment options. Lifestyle changes can have a significant impact; for instance, a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can enhance hair health. Over-the-counter products like minoxidil can stimulate hair growth, while prescription medications may also be available for more severe cases. Additionally, consider non-invasive treatments such as laser therapy or scalp massages. If you're open to it, hair transplant surgery is another option for restoration. Remember, the key is to remain positive and proactive while seeking solutions that work best for you.