CSGO Flares: Your Ultimate Esports Hub
Explore the latest news, tips, and insights from the world of CS:GO.
Blockchain: The New Frontier for Digital Trust
Discover how blockchain is revolutionizing digital trust and unlocking new possibilities for secure transactions and transparency!
How Blockchain Technology is Revolutionizing Digital Trust
Blockchain technology is fundamentally changing the way we establish and maintain digital trust in an increasingly interconnected world. By leveraging a decentralized and immutable ledger, blockchain solutions provide transparency and security that traditional systems often lack. Each transaction is recorded in a block and linked to the previous one, creating a chain of trustworthy data that is nearly impossible to alter. As more industries adopt this technology, from finance to supply chains, businesses and consumers can transact with confidence, knowing their data and assets are protected.
The application of smart contracts is further enhancing digital trust by automating agreements between parties without the need for intermediaries. These self-executing contracts reduce the potential for fraud and miscommunication, allowing for seamless transactions that are verified by the blockchain network. As organizations embrace this technology, we are likely to see an increase in efficiency and a reduction in costs. The revolution brought by blockchain is not merely a technological shift; it represents a transformative approach to trust, enabling a more transparent, equitable, and secure digital landscape for everyone.
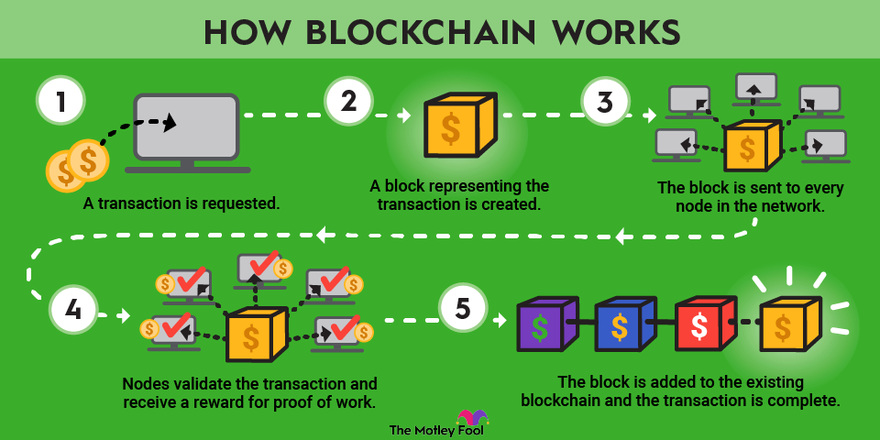
Exploring the Role of Decentralization in Building Trust through Blockchain
Decentralization plays a pivotal role in enhancing trust within the blockchain ecosystem by eliminating the need for central authorities. Traditionally, trust in transactions relies on intermediaries such as banks or payment processors. With blockchain technology, trust is built through a network of nodes that validate and record transactions transparently. This eliminates single points of failure and reduces the risk of fraud, as each participant in the network can independently verify the authenticity of transactions. As a result, users can engage in peer-to-peer transactions with a higher degree of confidence, knowing that they are backed by a decentralized consensus mechanism.
Moreover, the inherent transparency of blockchain systems fosters a sense of accountability among participants. Each transaction is recorded on a public ledger, allowing users to trace the history of exchanges without compromising privacy. This visibility encourages ethical behavior and discourages dishonest practices, further reinforcing trust within the network. As decentralization continues to gain traction across various industries, understanding its significance in building trust is crucial for both businesses and consumers. In an era where trust is paramount, embracing decentralized solutions could reshape our interactions and bolster confidence in digital transactions.
What Makes Blockchain a Secure Solution for Digital Identity?
Blockchain technology offers a robust framework for securing digital identities through its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional databases that are centralized and vulnerable to hacks, blockchain distributes data across a network of computers (nodes). This means that even if one node is compromised, the others remain intact, making it exceedingly difficult for attackers to manipulate or steal identity information. Additionally, each transaction or record added to the blockchain is encrypted and linked to the previous one, creating an immutable chain. This transparency and traceability foster trust among users, as they can verify the authenticity of their identities without relying on a single governing entity.
Furthermore, blockchain employs sophisticated cryptographic techniques that enhance security policies surrounding digital identities. Through the use of public and private keys, users maintain control over their data, allowing them to choose what information to share and with whom. This selective sharing minimizes the risk of identity theft, as individuals are not required to disclose sensitive personal data to third parties. The consensus mechanisms used in blockchain, whether through proof of work or proof of stake, further ensure that unauthorized changes to identity records are nearly impossible, thereby preserving the integrity of each digital identity stored on the network.